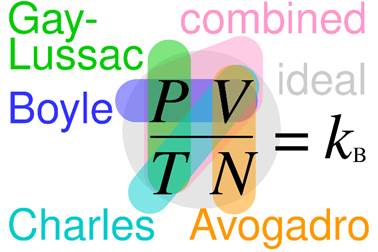Air Gases
-
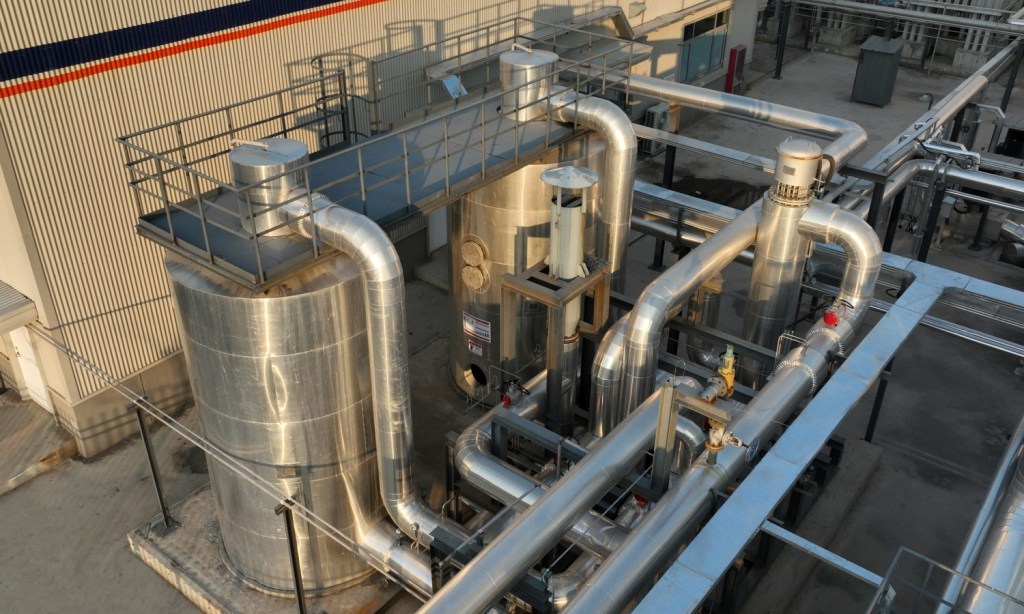
Unpacking the Cryogenic Air Separation Process – Purification
After a pre-cooling process, the atmospheric air still contains some impurities, such as carbon dioxide, hydrocarbons, moisture, etc. These impurities must be reduced to a certain value so that they will not bring any problems to the subsequent cooling and… Continue reading
-
Unpacking the Cryogenic Air Separation Process – Filtration, Compression, and Cooling
In a cryogenic air separation plant, air is separated into its components based on their boiling points at a very low temperature. The process flow diagram is rather complex and challenging for an undergraduate chemical engineering student. It consists of… Continue reading
-
The Ideal Gas Law: A Cornerstone of Thermodynamics
The ideal gas law is one of the foundational concepts in thermodynamics. While it is based on a simplified model, it continues to serve as a powerful tool in many industrial applications. What Defines an Ideal Gas? An ideal gas… Continue reading
-
Thermodynamics in Cryogenic Engineering: Why the Basics Still Matter
In the world of cryogenic air separation, it is easy to get caught up in complex machinery—compressors, turbines, heat exchangers—and forget the core science behind it all. But no matter how advanced the equipment, cryogenic processes are still grounded in… Continue reading
-
Atmospheric Air Composition
Atmospheric air surrounds both lands and oceans of the planet Earth. It is free, widely available, and acts as a main raw material for the air separation industries. In the 18th century, Joseph Priestley, Antoine Lavoisier, and Henry Cavendish conducted… Continue reading